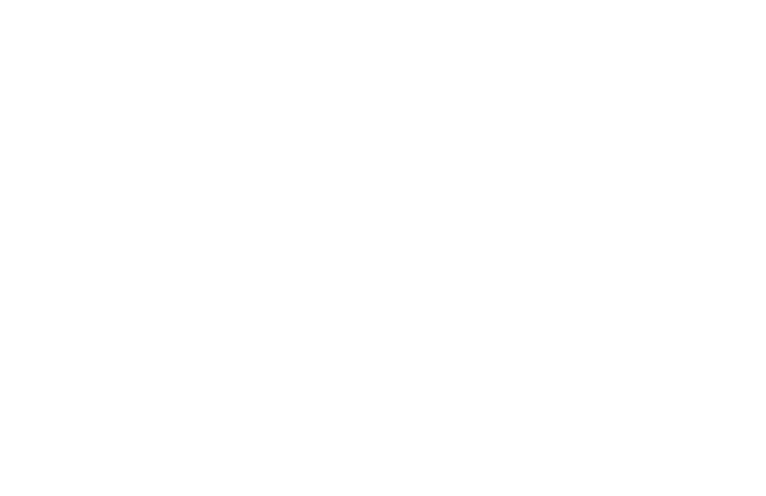
While the 36th European Water Polo Championships in Croatia and the Netherlands are coming near, let’s take a look back at history.
Here are some interesting facts, unusual details, and information about records throughout a 98-year-old history of the continental water polo championships.
From 4 to 32 teams
Only four teams participated in the 1st European Championships in Budapest in 1926. They played in one group by a league round-robin system. Hungary emerged as the champion after defeating Germany (8:1), Belgium (5:0), and Sweden (3:2). Germany won silver, and Sweden took bronze.
A total of 32 teams will compete at the 2024 European Championships because the number of female teams increased to 16.
In two countries for the second time
The 2024 European Championships in Croatia and the Netherlands will be the second water polo championships of the „Old Continent“ to be staged in two countries.
The first European Championship for ladies was held in 1985 in Oslo. That year, the men’s tournament was part of the European Aquatics Championships in Sofia.
Since the inauguration of the European Women’s Water Polo Championships, the men’s and women’s tournaments have been held in different cities four times.
In 1993, at the European Aquatics Championships in Great Britain, the men battled for medals in Sheffield and the women in Leeds.
Italy organized the 1999 European Championships – the men’s tournament was held in Firenze and the women’s in Prato. These two cities are approximately 30 km far from each other. That was the 1st European Water Polo Championships organized separately from the continental championships in all aquatic sports.
Four years later, Slovenia hosted the Europeans. Men played in Kranj and women in the country’s capital, Ljubljana.
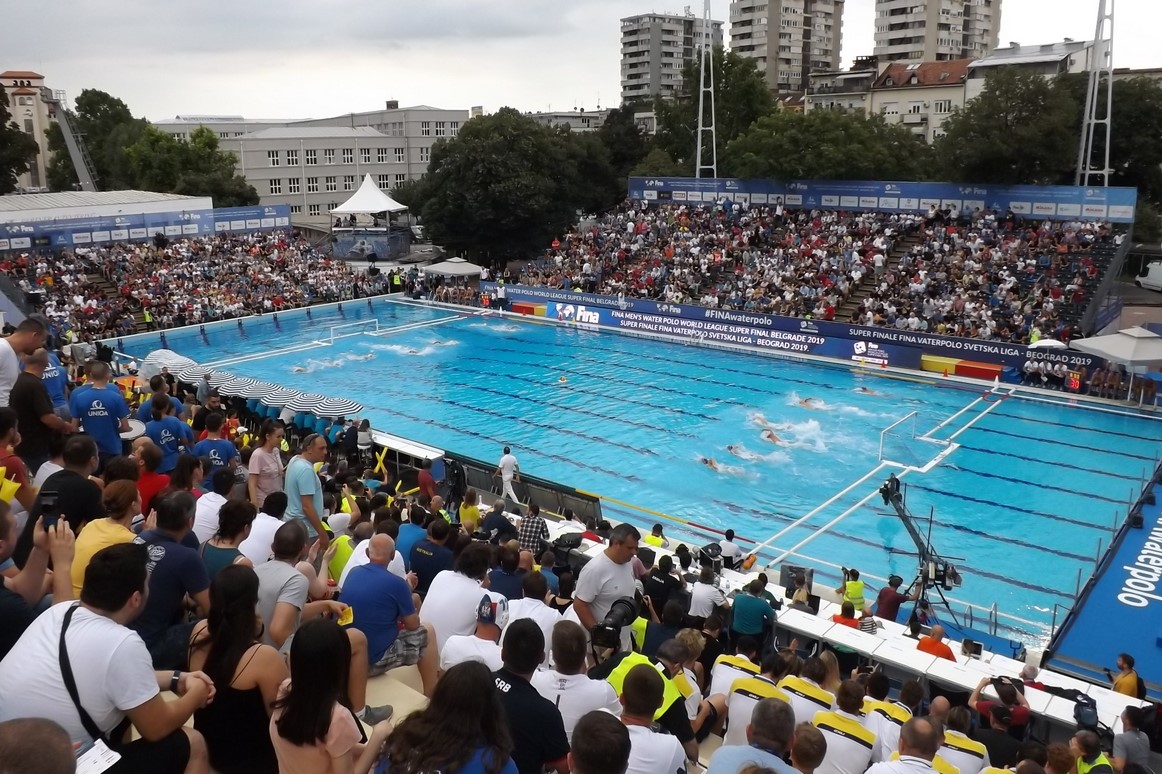

Tasmajdan pool, Belgrade
The previous championship that took place in two pools was the one in Belgrade in 2006. The men played in the Tasmajdan Pool, and the ladies played a few kilometers from there – in Banjica.
Three pools
The water polo tournament at the 1970 European Water Polo Championships was held in not one, not two, but three different pools! In addition to the Bernat Picornell Pools in the Monjuic Hill in Barcelona, the tournament was also held in the pools in the nearby Zaragoza and in a suburb of the Catalan capital.
But, all of these pools were used by athletes in other aquatic sports during the Championships.
Four years later, water polo players were provided with a separate pool for the first time, which was exclusively allocated to them throughout the tournament. The Stadionbad pool complex in Vienna hosted the 1974 European Championships, where every water sport was assigned its pool.
Championships in football stadium
The water polo tournament at the 1995 European Championships in Vienna was held in a football stadium – in the famous Prater. A temporary pool was installed on the athletic track. But, it turned out to be a bad idea. The stands weren’t close to the pool. The fans were only in one tribune. Most of the 50.000 seats in the stadium were empty, and it was impossible to create a good atmosphere.
35 gold, 36 silver and 34 bronze medals
Thirty-five editions of the European Men’s Championships have been held since 1926, but 36 silver and 34 bronze medals were awarded in the past 98 years.

Why?
Yugoslavia and the USSR shared the silver medal at the 1962 European Championships in Leipzig. The tournament was played in three group phases. There was no knockout round. The teams of the Soviet Union and Yugoslavia won three points each in the final group (the USSR had three draws, and Yugoslavia had one win, one draw, and one loss). The USSR’s goal difference was 7:7 and Yugoslavia’s 6:6. At that time, there were no today’s tie-breaking rules, and the two teams shared the silver medal, while the bronze wasn’t awarded. Hungary won gold.
17 teams in Utrecht
The record for the number of participating teams in a single tournament was set in Utrecht in 1966. Seventeen teams played in a nine-day competition. The Soviet Union won gold ahead of East Germany and Yugoslavia.
Interestingly, similarly to the previous Europeans in Leipzig, two medal winners had the same number of points in the final group. Unlike the tournament in Leipzig, they didn’t share a medal. The Soviet Union and East Germany won 4 points each. The USSR took gold, thanks to a win over Germany in the match that saw only one goal (1:0).
1st final in 1989
The first final games of the European Championships were played at the tournaments in Bonn in 1989. Until then, the teams battled through groups in round-robin formats (except for the 1927 Championships, which had a very unusual format).
West Germany narrowly beat Yugoslavia 10:9 in the first final for men, while the Netherlands defeated Hungary by three goals (14:11) in the first final game of the Women’s European Championships.
Golden goal
After the 1986 World Championships final in Madrid, where Yugoslavia won gold, beating Italy after eight extra-time periods (10:9), a “Golden Goal” rule was introduced in water polo. If the game after four quarters ended in a tie, a winner was a team that scored the first goal in the extra-time period(s).
Photo by Laszlo Balogh/Total Waterpolo
The first-ever Men’s European Championships final in Bonn in 1989 saw West Germany defeating Yugoslavia 10:9 with a “Golden Goal”. It was Germany’s third and, so far, last gold medal at the European Championships. This was the only European Championships final in which the champion was decided using the “Golden Goal” rule, which was scrapped from the international water polo rules several years later.
Three medal matches and repechage in Bologna
The match between Germany and Yugoslavia in Bonn was the first European Championships final, but the first gold-medal match was played at the 2nd ECH in Bologna in 1927.
The competition formula in Bologna was like in the tournaments in wrestling, with a repechage. It is very unusual and complicated for team sports. So, the gold-medal match wasn’t the final as we know it today. Three medal games were played in Bologna.
Twelve teams participated in a tournament played in a knockout format. The winners of the six matches in the first round advanced to the second. Hungary, France, and Sweden beat their rivals in the 2nd round. Hungary skipped the third round as the defending champion and advanced to the gold medal match. France joined the Hungarians after beating Sweden in the third round.
Hungary won gold, defeating France 3:1 in the match for 1st place, but France didn’t secure a medal with that loss. It only qualified for the 2nd-place game.
Photo: Total Waterpolo
The teams that were beaten by Hungary played in the repechage for 2nd place. The teams defeated by France had a chance in the repechage for 3rd place. France beat Belgium in the 2nd-place game to win the silver medal. After that, on the same day, Belgium defeated Sweden in the bronze-medal match. The silver and bronze medal winners were decided two days after Hungary defended the European crown.
The round-robin formats were applied throughout all tournaments from the next Europeans in Paris in 1931 until 1989.
Hungary missed only one European Championships
None of the countries participated in all the previous 35 editions of the European Championships.
Hungary is the record-holder with 34 appearances.
The Hungarians missed only the 7th ECH, held in Vienna in 1950. Those were the early years of the Cold War and high political tensions.
Initially, Budapest was awarded the organization of the 1950 Europeans. But two years before, LEN requested the Hungarian authorities to provide guarantees for all athletes, judges, and foreign fans to enter the country without visas. The Hungarian Government had a short period to decide if it was possible. Since LEN didn’t want (or wasn’t able) to wait, Budapest was stripped of the opportunity to host the championship, and Vienna was selected as the new venue.
At that time, Vienna and the entire Austria were divided into four zones and jointly occupied by the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, the United States, and France.
The Championships were held in one of the parts controlled by the countries that were members of NATO, founded in the previous year. The athletes from Eastern Block countries, including the Hungarians, didn’t come to Vienna.
The only socialist country that participated was Yugoslavia, which was never a member of either NATO or the Warsaw Pact (founded in 1955). The Yugoslav team won bronze.
Seven teams played at the tournament, and the Netherlands won its first and, so far, the only gold medal in the male tournament.
Great mistake by Great Britain
An interesting fact about the 1950 European Championships is that the team of one of the countries that founded NATO withdrew from the competition because of a “political mistake.”
The British water polo team, swimmers, and divers didn’t participate in the Europeans in Vienna as they believed the Championships would be held in the Soviet-occupied zone.
All medal winners, Men
1926 Budapest: Hungary, Sweden, Germany
1927 Bologna: Hungary, France, Belgium
1931 Paris: Hungary, Germany, Austria
1934 Magdeburg: Hungary, Germany, Belgium
1938 London: Hungary, Germany, Netherlands
1947 Monte Carlo: Italy, Sweden, Belgium
1950 Vienna: Netherlands, Sweden, Yugoslavia
1954 Torino: Hungary, Yugoslavia, Italy
1958 Budapest: Hungary, Yugoslavia, USSR
1962 Leipzig: Hungary, Yugoslavia and USSR (shared 2nd place)
1966 Utrecht: USSR, West Germany, Yugoslavia
1970 Barcelona: USSR, Hungary, Yugoslavia
1974 Vienna: Hungary, USSR, Yugoslavia
1977 Jonkoping: Hungary, Yugoslavia, Italy
1981 Split: West Germany, USSR, Hungary
1983 Roma: USSR, Hungary, Spain
1985 Sofia: USSR, Yugoslavia, West Germany
1987 Strasbourg: USSR, Yugoslavia, Italy
1989 Bonn: West Germany, Yugoslavia, Italy
1991 Athens: Yugoslavia, Spain, USSR
1993 Sheffield: Italy, Hungary, Spain
1995 Vienna: Italy, Hungary, Germany
1997 Sevilla: Hungary, Yugoslavia, Russia
1999 Florence: Hungary, Croatia, Italy
2001 Budapest: Yugoslavia, Italy, Hungary
2003 Kranj: Serbia & Montenegro, Croatia, Hungary
2006 Belgrade: Serbia, Hungary, Spain
2008 Malaga: Montenegro, Serbia, Hungary
2010 Zagreb: Croatia, Italy, Serbia
2012 Eindhoven: Serbia, Montenegro, Hungary
2014 Budapest: Serbia, Hungary, Italy
2016 Belgrade: Serbia, Montenegro, Hungary
2018 Barcelona: Serbia, Spain, Croatia
2020 Budapest: Hungary, Spain, Montenegro
2022 Split: Croatia, Hungary, Spain
Medal table: 1. Hungary 26 (13 gold, 7 silver, 6 bronze), 2. USSR 10 (5, 3, 2), 3. Serbia 7 (5, 1, 1), 4. Italy 11 (3, 2, 6), 5. Croatia 5 (2,2,1), 6. FR Yugoslavia/Serbia and Montenegro 3 (2, 1, 0), 7. West Germany 3 (2, 0, 1), 8. SFR Yugoslavia 12 (1, 7, 4), 9. Montenegro 4 (1, 2, 1), 10. Netherlands 2 (1, 0, 1), 11. Spain 7 (0, 3, 4), 12. Germany 5 (0, 3, 2), 13. Sweden 3 (0, 3, 0), 14 – 15. East Germany 1 (0, 1, 0) and France 1 (0, 1, 0), 16. Belgium 3 (0, 0, 3), 17 – 18. Austria 1 (0, 0, 1) and Russia 1 (0, 0, 1).
Note: The first criterion for the rankings is the number of titles, and the second is the number of silver medals.
(The list of the medal winners’ in the women’s tournament in the 2nd part)






